Chocolate. Just the word conjures images of velvety bites, the sweet comfort after a long day, and indulgent moments that seem almost sinful. Millions around the globe savor chocolate daily, treating it as a reward, a ritual, or a pure source of joy. But hidden behind that luscious taste lies a darker story—one that merges chemistry, botany, toxicology, and a dash of myth. Could your favourite chocolate actually be toxic? The answer is far more complex than a simple “yes” or “no.” Let’s unwrap this story, bite by bite.
The Cocoa Bean: Sweet Beginnings, Bitter Truths
Chocolate’s journey starts with the cocoa bean, scientifically known as Theobroma cacao, literally meaning “food of the gods.” Native to Central and South America, these beans have been cultivated for thousands of years, revered by ancient civilizations for their medicinal and ritualistic properties. However, nature has its protective mechanisms, and the cocoa bean is no exception.
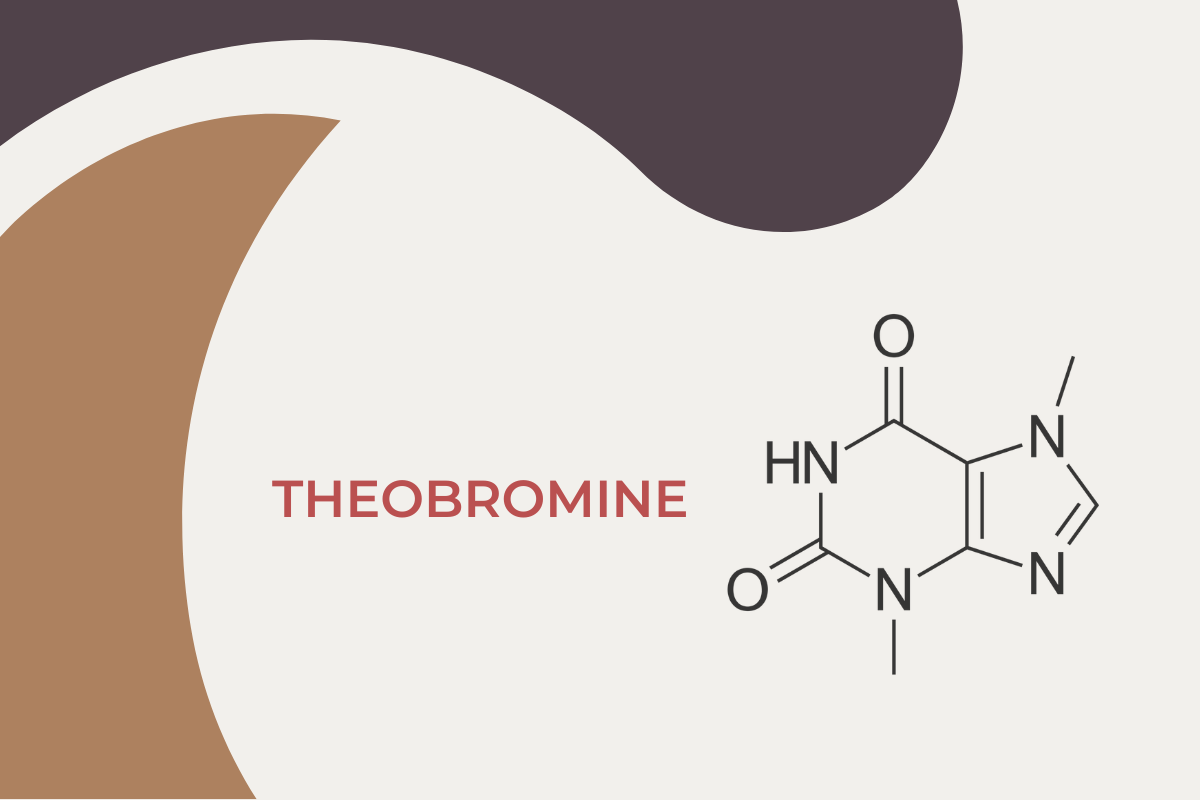
Cocoa naturally contains compounds called methylxanthines, primarily theobromine and caffeine. These alkaloids act as natural pesticides, deterring insects and herbivores. While humans tolerate them relatively well, the line between a pleasurable stimulant and a toxin is thinner than one might imagine.
Theobromine is chemically similar to caffeine but metabolizes more slowly in the human body, giving chocolate its lingering stimulant effect. In moderation, this can boost alertness and even mood. But too much? That’s where toxicity begins to loom.
How Chocolate Affects Humans
For most people, chocolate is perfectly safe, even beneficial. Studies suggest dark chocolate in particular can improve heart health, thanks to flavonoids—antioxidant compounds that support vascular function. It can enhance mental alertness, elevate mood via serotonin modulation, and even provide trace minerals like magnesium, iron, and zinc.
Yet, the risk is dose-dependent. The average dark chocolate bar contains roughly 200–500 mg of theobromine per 100 grams. For an average adult, toxic effects are unlikely unless consumption skyrockets to kilograms at a time. Still, certain populations, like children, may be more sensitive to the stimulant effects, resulting in insomnia, rapid heartbeat, or gastrointestinal upset.
Interestingly, the darker the chocolate, the higher the concentration of theobromine—and the greater the potential risk if consumed excessively. White chocolate? Virtually negligible in theobromine, but not entirely free from concern.
When Chocolate Turns Dangerous
Human toxicity aside, chocolate becomes genuinely concerning for pets. Dogs, cats, and some wildlife metabolize theobromine much more slowly than humans. Even small amounts can lead to theobromine poisoning, causing symptoms ranging from hyperactivity and vomiting to seizures and, in severe cases, death.
Beyond theobromine, chocolate can also harbor other risks:
- Heavy Metal Contamination: Cocoa plants can absorb cadmium and lead from the soil. Chronic exposure can impact kidney function and neurological development. Certain dark chocolates from high-cadmium regions have raised alarms.
- Microbial Hazards: Improperly stored chocolate can develop mold or host bacteria. While rare, certain molds produce mycotoxins, adding another layer of risk.
- Added Ingredients: Nuts, dairy, and artificial sweeteners like xylitol (toxic to dogs) can complicate chocolate’s safety profile.
This is not to panic chocolate lovers—these hazards are typically controlled in commercial production. Yet, the fact remains that chocolate is not purely a harmless treat.
The Chemistry Behind the “Toxic” Label
So, what actually makes chocolate toxic? The main culprit is theobromine, but other compounds also contribute. Let’s break them down:
- Theobromine: A mild stimulant in humans but potent in animals. In humans, doses above 1,000 mg per day may cause nausea, sweating, and heart palpitations. In dogs, even 100 mg/kg body weight can be fatal.
- Caffeine: Present in smaller amounts, caffeine contributes to insomnia, anxiety, and heart palpitations if overconsumed.
- Oxalates: Found naturally in cocoa, oxalates can contribute to kidney stone formation in susceptible individuals.
- Acrylamide: A byproduct of roasting cocoa beans, acrylamide is classified as a potential carcinogen in high doses, though typical chocolate consumption remains far below concerning levels.
- Heavy Metals: Cadmium and lead, as previously mentioned, can accumulate in the body over time, creating long-term risks.
In short, chocolate is a cocktail of compounds that can oscillate between beneficial and toxic depending on dose, individual sensitivity, and species.

The Dark Side: Industrial Production and Hidden Dangers
Commercial chocolate often undergoes extensive processing, which influences its safety and toxicity. Consider the following:
- Alkalization (Dutch Processing): This technique reduces bitterness but also alters antioxidant content. While not toxic per se, it changes the chemical balance of the final product.
- Additives and Preservatives: Many chocolate bars contain emulsifiers, artificial flavors, and preservatives. Some, like soy lecithin, are generally regarded as safe, but others may trigger allergic reactions or digestive sensitivity.
- Contaminant Exposure: In large-scale processing, machinery and storage conditions can introduce traces of metals, bacteria, or mold. Regulatory standards minimize this risk, but it’s never zero.
Moreover, imported chocolates may vary greatly depending on the agricultural practices in the source country. Soil contamination, pesticide use, and storage conditions can all influence the chemical profile of cocoa beans.
Myth-Busting Chocolate Toxicity
There’s a lot of exaggeration surrounding chocolate’s risks. Let’s address some common misconceptions:
Myth 1: All chocolate is toxic to humans.
Reality: Only in extremely large quantities. For most adults, chocolate is not only safe but can be part of a healthy diet.
Myth 2: Dark chocolate is more dangerous than milk chocolate.
Reality: Dark chocolate has higher theobromine levels, but toxicity in humans is still rare unless consumed in enormous amounts. Its health benefits often outweigh potential risks.
Myth 3: White chocolate is completely safe.
Reality: White chocolate lacks theobromine but contains sugar, fats, and sometimes heavy metals. “Safe” does not mean health-neutral.
Myth 4: Chocolate poisoning is a common occurrence.
Reality: Human chocolate poisoning is extremely rare. Most cases are anecdotal or involve children with preexisting health conditions. The real concern is for pets.
Chocolate and Health: A Balancing Act
Chocolate can be both indulgent and beneficial when consumed wisely. Here’s how to enjoy it safely:
- Moderation is Key: One or two small squares of dark chocolate per day typically falls within safe limits.
- Mind the Additives: Look for chocolates with minimal processing and lower sugar content. Organic or single-origin chocolates may reduce the risk of heavy metals.
- Consider Individual Sensitivity: Children, pregnant women, and individuals with heart conditions may need to limit intake.
- Avoid Giving Chocolate to Pets: Dogs, cats, and other small mammals metabolize theobromine slowly, making even tiny amounts dangerous.
Interestingly, research is exploring how certain compounds in chocolate can promote cardiovascular and cognitive health. Flavanols in cocoa may support vascular function, reduce blood pressure, and even improve insulin sensitivity. This duality—pleasure and risk—is what makes chocolate fascinating from a biochemical perspective.
Beyond the Bar: Chocolate in Other Forms
Chocolate exists in a variety of forms beyond the classic bar:
- Hot Cocoa: Often less concentrated in theobromine but high in sugar.
- Cocoa Powder: Extremely concentrated, so dosage matters if consumed in recipes.
- Chocolate Liquor: Pure, unsweetened chocolate that is technically toxic in large doses.
- Baking Chocolate: Very high in theobromine; consuming it directly in large quantities is dangerous.
Even chocolate-flavored products like ice cream or beverages carry the same caveats, albeit at lower risk levels. When chocolate becomes a recipe ingredient, its concentration and serving size must be considered carefully.
Pop Culture and Chocolate’s “Toxic” Reputation
Chocolate’s reputation as both a divine pleasure and a potential poison has fascinated humans for centuries. Ancient Mesoamerican cultures used cocoa as medicine and currency, sometimes warning against excessive consumption. In modern times, chocolate often symbolizes indulgence, guilt, and the thrill of forbidden pleasure.
Movies, literature, and marketing have played with the idea of chocolate as a double-edged sword. From mysterious chocolate factories to satirical “death by chocolate” scenarios, society loves to flirt with the idea that something so sweet could harbor hidden danger.
Scientific Studies and Chocolate Toxicology
Recent studies in toxicology have focused on:
- Theobromine Pharmacokinetics: Understanding how theobromine is metabolized in humans versus animals.
- Heavy Metal Accumulation: Measuring cadmium and lead levels in chocolate from various countries.
- Long-term Health Effects: Evaluating chocolate consumption in relation to cardiovascular health, diabetes, and cognitive function.
- Dose Thresholds: Determining the point at which chocolate shifts from beneficial to toxic in humans.
The consensus? Chocolate is safe for humans in moderation, but vigilance is warranted in terms of concentration, quality, and special populations.
Tips for Choosing Safe Chocolate
When shopping for chocolate with safety in mind:
- Check Labels: Look for cocoa percentage, ingredient list, and origin.
- Opt for Trusted Brands: Established brands often have stricter quality control.
- Moderate Dark Chocolate Intake: Higher cocoa content means higher theobromine.
- Be Wary of Exotic Additives: Unfamiliar nuts, fruits, or flavorings can cause reactions or carry contaminants.
- Consider Organic or Single-Origin: Reduces the likelihood of chemical exposure.
- Store Properly: Keep chocolate in cool, dry conditions to prevent mold and rancidity.
Conclusion: Pleasure and Caution in Every Bite
Could your favourite chocolate actually be toxic? Technically, yes—but for most humans, the risks are minimal and easily managed. Chocolate’s unique chemical profile offers both pleasure and pharmacological activity, a combination that has fascinated scientists, historians, and chocolate lovers alike.
The real danger lies less in everyday indulgence and more in extreme consumption, poor-quality products, and the temptation to share with pets. By understanding what’s inside that luscious bar—the theobromine, caffeine, flavonoids, and potential contaminants—you can enjoy chocolate responsibly, savoring its pleasures without fear.
Chocolate is a marvel of nature and human ingenuity: complex, delightful, and yes, slightly dangerous in just the right doses. The “toxicity” is real but manageable. With awareness and moderation, you can continue to enjoy the food of the gods without worry—each bite a blend of science, history, and sheer bliss.























